Books in series

Tarta róża
2017

Inna wyspa
2018

I znów zaczyna się przeszłość
2018

Na nitce deszczu
2019

Perłopław na piasku. Haiku - images
2019

Ułamki
2019

Człowiek
2020

Wsłuchać się w szum wód
2021

Rdza żelazo zmocuje
2021

Chwila szczęścia
2021

Jestem gotowa
2022

Chłopiec
2022
Authors

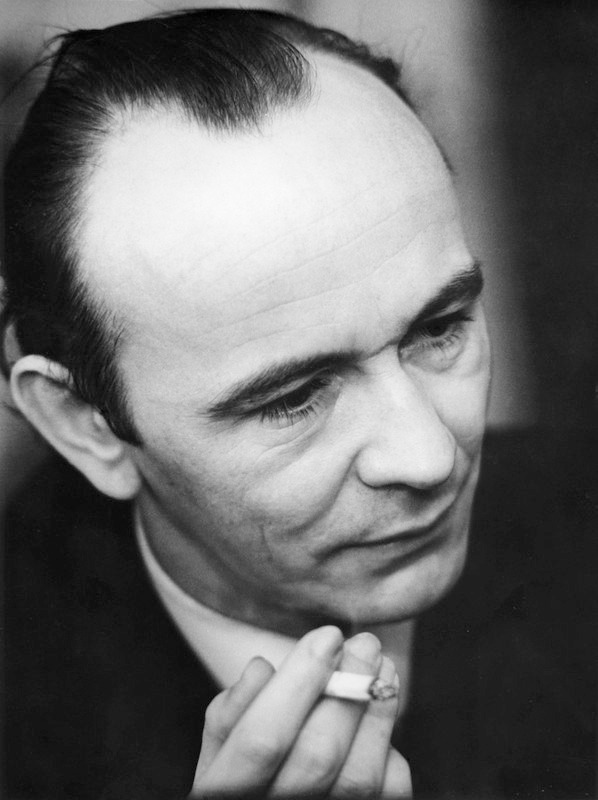
Aleksander Wat, (born Aleksander Chwat to a Jewish father and a Polish mother) was a Polish poet, writer and art theoretician, one of the precursors of Polish futurism movement in early 1920s. In 1919 he was among the young poets to proclaim the advent of new, futuristic poetry. The following year he published the first set of his poems, which gained much popularity among the supporters of the new trends in literature of the epoch. Until 1922 he was one of the creators of the Nowa Sztuka ("New Art") monthly, and then Almanachy Nowej Sztuki and Miesięcznik literacki. Initially a Communist, until 1931 he was also one of the main journalists of the Marxist Tygodnik literacki.

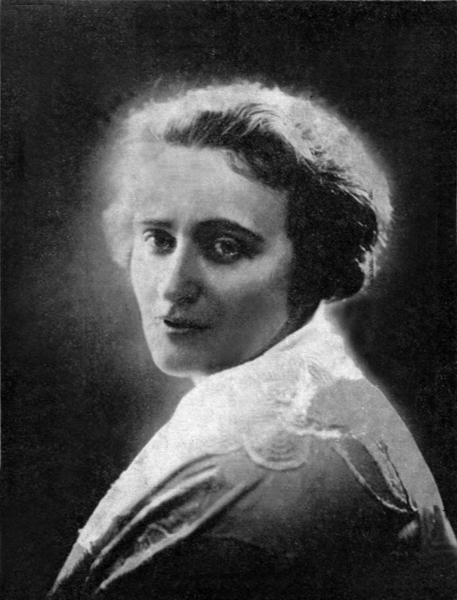
Anna Świrszczyńska (also known as Anna Swir) was a Polish poet whose works deal with themes including her experiences during World War II, motherhood, the female body, and sensuality. Świrszczyńska was born in Warsaw and grew up in poverty as the daughter of an artist. She began publishing her poems in the 1930s. During the Nazi occupation of Poland she joined the Polish resistance movement in World War II and was a military nurse during the Warsaw Uprising. She wrote for underground publications and once waited 60 minutes to be executed. Czesław Miłosz writes of knowing her during this time and has translated a volume of her work. Her experiences during the war strongly influenced her poetry. In 1974 she published Building the Barricade, a volume which describes the suffering she witnessed and experienced during that time. She also writes frankly about the female body in various stages of life.

To a Pole, the name Adam Mickiewicz is emblematic of Polishness and greatness. What Homer is to the Greeks, or Shakespeare to the English, Mickiewicz is to the Poles. He is a cultural icon, a name inextricably connected with Polish literature and history, and one mentioned with pride. Mickiewicz stands out in the consciousness of Poles both as a man of letters and a political leader. Despite his unquestionable status and fame, however, much of Mickiewicz's biography is shrouded in mystery. Even the generally accepted date of his birth, December 24. 1798, is uncertain, since it hasn't been determined whether it refers to the Gregorian or the Julian calendar. Nor has it been established conclusively whether Mickiewicz was born in Nowogrodek or at Zaosie, a mile or so apart. Many biographical facts, particularly those pertaining to his relationships with women, were deliberately obscured to preserve a flawless public image of the poet. Likewise, his interest in mysticism and involvement in mystical cults tended to be minimized, especially during the years of Communist rule in Poland when the official line was to shun spirituality of any kind, not to expose the poet to ridicule. Mickiewicz's son. Władysław, can be held partially responsible for this state of affairs, but he is not the only one. Having gained control of his father's papers after the poet's death, Władysław Mickiewicz destroyed various documents which might have potentially tarnished his father's public image. Likewise, many critics and scholars tended to overlook significant facts in the poet's biography, as well as significant themes and issues in his writing, to sustain the idealized view of Mickiewicz as a Polish national bard. This tendency to carefully "whitewash" Mickiewicz is hardly surprising. Born three years after the final partition of Poland, Mickiewicz became a spiritual leader of the Polish nation. An ardent patriot, he animated the Polish national spirit through his poetic, dramatic and political writings, providing hope and spiritual sustenance to Poles under the Russian, Prussian and Austrian rule, as well as to the many exiles, particularly the emigré circles in Paris, where he settled in 1832. Given the history of Poland and the long streak of political oppression and subjugation, the need for heroes and the idealization of Mickiewicz as a leader are perfectly understandable. Yet already in the 1930s, there were critical voices against the bowdlerization of Mickiewicz's work (since some editions of his works eliminated the more racy passages) and objections were raised against the cover-up in renditions of his biography. The prominent critic, Tadeusz Boy-Źieleński, for instance, in his work "Brązownicy" objected to the distortions of facts and the "sins of omission" in critical writings on Mickiewicz. In recent years, a much more vast and thorough re-examination of Mickiewicz' life and oeuvre has occurred. This is partially due to the overall re-examination of Polish history and Polish literary tradition after the collapse of Communism and, generally. a much greater openness in discussions of various issues previously relegated to the sphere of national taboos. Thus, much has been written lately about the white spots in Mickiewicz's biography. particularly about his mystical leanings and the Jewish origin of his mother. The evidence of Mickiewicz's fascination with mysticism is overwhelming, and there is some basis for the allegation of his mother's Jewishness. (quoted from Regina Grol's piece posted on InfoPolan, University of Buffalo's website; for continuation see link below)

Juliusz Słowacki ['juljuʂ swɔ'vatski] (4 September 1809 in Kremenets, Volhynia, Russian Empire now in Ukraine – 3 April 1849 in Paris) was a noted Polish Romantic poet, considered to be one of the "Three Bards" of Polish literature. His works often feature elements of Slavic pagan traditions, mysticism, and Orientalism. Life and work Influenced largely by Byron and Shakespeare, Słowacki's early work was often historical in nature, combining exotic locales (as in Arab) and tragedy (as in Maria Stuart). His work took on a more nationalist tone following the failed November Insurrection of 1830 - 1831. Like many of his countrymen, he decided to emigrate to France as a political refugee. Ironically, the first collections of poems he produced in France were unpopular in his native Poland, as they failed to capture the sentiment of the people living under Russian occupation. It was the French authorities which deemed them too nationalist; following a trip to Geneva in 1832, he was denied the right to return to France as part of a larger program to rid the country of the potentially subversive Polish exiles who had settled there. A third volume of his works, produced in Geneva, was far more nationalist in tone, and he began to win recognition in his homeland. In 1836, Słowacki embarked on a journey throughout Italy, Greece, Egypt and Palestine, which he described in his epic poem "Podróż do Ziemi Świętej z Neapolu". In 1844, he wrote Genezis z Ducha, an exposition of his philosophical ideas (called genesic idea) according to which the material world is an expression of an ever-improving spirit capable of progression into constantly newer forms. It was at this time that he attached himself to a group of likeminded young exiles, determined to return to Poland and win its independence. One of his friends was the pianist and composer Frédéric Chopin. The group travelled to Poznań, then under Prussian control. He participated in the Wielkopolska Uprising of 1848, addressing the National Assembly (Komitet Narodowy w Poznaniu) on 27 April. "I tell you," he declared as the rebels faced military confrontation with the Prussian Army, "that the new age has dawned, the age of holy anarchy." By 9 May, the revolt was crushed. Arrested by the Prussian police, Słowacki was sent back to Paris. On his way there, he passed through Wrocław, where he was reunited with his mother, whom he had not seen for almost twenty years. He died in Paris the following year, and was buried in the Montmartre. In 1927, some eight years after Poland regained her independence, the Polish government requested that Słowacki's remains be moved to Wawel castle in Krakow. He was reinterred near his old rival, Adam Mickiewicz. Long after his death, Słowacki acquired the reputation of national prophet. His poem "Papież Słowiański" (The Slavic Pope), published in 1848, was believed to foretell the ascension, in 1978, of Karol Wojtyła to the throne of St. Peter as Pope John Paul II. In 2009 Faye Dunaway starred in film "The Bait" by Polish film director and producer Dariusz Zawislak. "The Bait" is a contemporary version of the drama, "Balladyna."